 Henri-Émile-Benoît Matisse was a French artist, known for his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known primarily as a painter.
Henri-Émile-Benoît Matisse was a French artist, known for his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known primarily as a painter.
- Born: December 31, 1869,
Le Cateau-Cambrésis, France - Died: November 3, 1954, Nice, France
Henri Matisse worked as a law clerk in Paris before starting to paint in the winter of 1889, during his convalescence from appendicitis. He studied under the academic painter (Adolphe) William Bouguereau and then Gustave Moreau, in whose class he met several artists who would become known as ‘les fauves’ (wild beasts). Matisse became a member of the official Salon in 1896, and seemed destined for a career as a successful but conservative painter. He became influenced by Impressionism and Neo-Impressionism before turning to the works of Cézanne. Together with Derain and Maurice de Vlaminck, he was pivotal in developing the highly coloured, expressive style that came to be known as Fauvism. After the First World War, his painting became more naturalistic and intimate. He was evidently seeking to reconcile the revolutionary features of Fauvism with the easel-painting tradition – and to celebrate the proprieties and pleasures of middle-class domesticity in peace-time

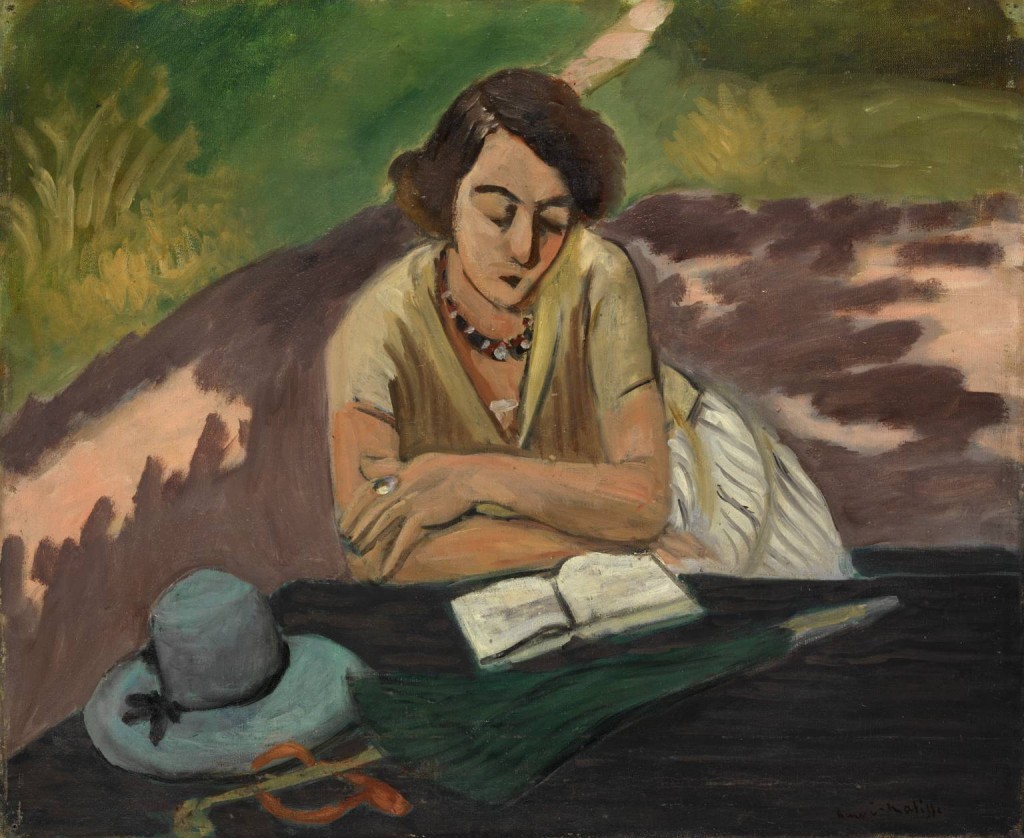
Oil on canvas. 50.0 x 61.0cm
Musée de l’Orangerie, Paris
Matisse’s ‘odalisques’ display the artist’s passion for decorative pattern and motifs. The artist visited the French colonies in North Africa (Algeria in 1906 and Morocco in 1912–13) where the brilliant light, exotic environment and Moorish architecture inspired a new body of work. His odalisques have been described by art historian Roger Benjamin as ‘elaborate fictions’ in which the artist re-created the image of the Islamic harem using French models posed in his Nice apartment. The fabrics, screens, carpets, furnishings and costuming recalled the exoticism of the ‘Orient’ and provided a theme for Matisse’s preoccupation with the figure and elaborate pattern



Henri Emile Benoît Matisse was born in a tiny, tumbledown weaver’s cottage on the rue du Chêne Arnaud in the textile town of Le Cateau-Cambrésis at eight o’clock in the evening on the last night of the year, 31 December 1869 (Le Cateau-Cambrésis is in the extreme north of France near the Belgian border). The house had two rooms, a beaten earth floor and a leaky roof. Matisse said long afterwards that rain fell through a hole above the bed in which he was born. Matisse’s ancestors had lived in the area for centuries before the convulsive social and industrial upheavals of the nineteenth century. Matisse grew up in a world that was still detaching itself from a way of life in some ways unchanged since Roman times. The coming of the railway had put Bohain on the industrial map, but people still traveled everywhere on foot or horseback.
Matisse’s father, Émile Hippolyte Matisse, was a grain merchant whose family were weavers. His mother, Anna Heloise Gerard, was a daughter of a long line of well-to-do tanners. Warmhearted, outgoing, capable and energetic, she was small and sturdily built with the fashionable figure of the period: full breasts and hips, narrow waist, neat ankles and elegant small feet. She had fair skin, broad cheekbones and a wide smile. “My mother had a face with generous features,” said her son Henri, who always spoke of her with particular tenderness of the sensitivity. Throughout the forty years of her marriage, she provided unwavering, rocklike support to her husband and her sons. Matisse later said: “My mother loved everything I did.” He grew up in nearby Bohain-en-Vermandois, an industrial textile center, until the age of ten, when his father sent him to St. Quentin for lycée.
Anna Heloise worked hard. She ran the section of her husband’s shop that sold housepaints, making up the customers’ orders and advising on color schemes. The colors evidently left a lasting impression on Henri. The artist himself later said he got his color sense from his mother, who was herself an accomplished painter on porcelain, a fashionable art form at the time. Henri was the couple’s first son.
The young Matisse was an awkward youth who seemed ill-adapted to the rigors of the North; in particular, he hated the gelid winters. He was a pensive child and by his own account he was a dreamy, frail and not outstandingly bright. In later life he never lost his feeling for his native soil, for seeds and growing things he had encountered in his youth. The fancy pigeons he kept in Nice more than half a century after he left home recalled the weavers’ pigeon-lofts tucked away behind even the humblest house in Bohain.
Matisse’s childhood memories were of a stern upbringing. “Be quick!” “Look out!” “Run along!” “Get cracking!” were the refrains that rang in his ears as a boy. In later years when survival itself depended on habits of thrift and self-denial, the artist prided himself on being a man of the North. When Matisse in turn had children of his own to bring up, he chided himself for any lapse in discipline or open display of tenderness as weakness on his part.
In 1887 he went to Paris to study law, working as a court administrator in Le Cateau-Cambrésis after gaining his qualification. Although he considered law as tedious, he nonetheless passed the bar in 1888 with distinction and began his practice begrudgingly. Once Matisse finished school, his father, a much more practical man, arranged for his son to obtain a clerking position at a law office.

Matisse’s discovery of his true profession came about in an unusual manner. Following an attack of appendicitis, he began to paint in 1889, when his mother had brought him art supplies during the period of convalescence. He said later, “From the moment I held the box of colors in my hands, I knew this was my life. I threw myself into it like a beast that plunges towards the thing it loves.” Matisse’s mother was the first to advise her son not to adhere to the “rules” of art, but rather listen to his own emotions. Matisse was so committed to his art that he later extended a warning to his fiancée, Amélie Parayre, whom he later married: “I love you dearly, mademoiselle; but I shall always love painting more.” Matisse had discovered “a kind of paradise” as he later described it. His drastic change of profession deeply disappointed his father.
Two years later in 1891 Matisse returned to Paris to study art at the Académie Julian and became a student of William-Adolphe Bouguereau. After a discouraging year at the Académie Julian, he left in disgust at the overly perfectionist style of teaching there. Afterwards he trained with Gustave Moreau, an artist who nurtured more progressive leanings. In both studios, as was usual, students drew endless figure studies from life. From Bouguereau, he learned the fundamental lessons of classical painting. His one art-schooled technical standby, almost a fetish, was the plumb line. No matter how odd the angles in any Matisse, the verticals are usually dead true. Moreau was a painter who despised the “art du salon”, so Matisse was destined, in a certain sense, to remain an “outcast” of the art world. He initially failed his drawing exam for admission to the École des Beaux-Arts, but persisted and was finally accepted.
Matisse began painting still-lives and landscapes in the traditional Flemish style, at which he achieved reasonable proficiency. Most of his early works employ a dark palette and tend to be gloomy. Chardin was one of Matisse’s most admired painters having made four the French still-life master paintings in the Louvre. Although he executed numerous copies after the old masters he also studied contemporary art. His first experimentations earned him a reputation as the rebellious member of his studio classes.
In 1896, Matisse was elected as an associate member of the Société Nationale, which meant that each year he could show paintings at the Salon de la Sociétéwithout having to submit them for review. In the same year he exhibited 5 paintings in the salon of the Société Nationale des Beaux-Arts, and the state bought two of his paintings. This was the first and almost only recognition he received in his native country during his lifetime. In 1897 and 1898, he visited the painter John Peter Russellon the island Belle Île off the coast of Brittany. Russell introduced him to Impressionism and to the work of Van Gogh who had been a good friend of Russell but was completely unknown at the time. Matisse’s style changed completely, and he would later say “Russell was my teacher, and Russell explained color theory to me.” Matisse also observed Russell’s and other artists’ stable marriages. This probably influenced him to find in Amélie Noellie Parayre, his future wife, his anchor.
The Dinner Table (1897) was Matisse’s first masterpiece, and he had spent the entire winter working on the oeuvre. Though the Salon displayed the piece, they hung the work in a poor location, disgusted by what they considered its radical, Impressionist aspects.
Caroline Joblaud was Matisse’s early lover for four years during his initial struggles to affirm his artistic direction and professional career. Caroline (also called Camille) gave Matisse his first daughter Marguerite in 1894, who after Matisse’s marriage to Amélie Noellie Parayre was warmly accepted contrary to conventional hostility such arrangements provoked. Caroline posed various times for the artist’s compositions while Marguerite served many times as a model for Matisse throughout his life.

The Matisses of Bohain and the Parayres of Beauzelle had outwardly nothing in common, and there was no reason why Matisse and Amélie should ever have met. But in October 1897 Matisse went to a wedding in Paris and happened to sit next to her at the uproarious banquet that followed. There had been no banal flirtation between them, even when the wine flowed, each recognized the other as true metal, and when they got up from the table she held out her hand to Henri Matisse in a way that he never forgot. Matisse at that time was not yet the professorial figure of legend. He was known as a prankster, as a ribald and anti-clerical songster, and as someone who had once broken up a café concert performance just for the hell of it. Amélie’s relatives operated at that time within a social, intellectual, and political context of which Matisse had had no previous experience. They stood for free thinking, for the separation of church and state, and for the secularization of the French educational system. Her family, better off that that of Matisse, provided the support he needed for the budding artist. When Matisse married Amélie in January 1898, they had been introduced only three months after.
Amélie’s Aunt Noélie and two of her brothers ran a successful women’s shop called the Grande Maison des Modes. Before her marriage, Amélie had shown a gift for designing, making, and modeling hats for a fashionable clientele. In June 1899, she found a partner and opened a shop of her own on the rue de Châteaudun. This allowed Henri and herself to live, with Marguerite, in a tiny two-room apartment on the same street. Madame Matisse, fervently loyal, would play a fundamental role in the life and career of the artist for more than 40 years. Marguerite was to become her father’s lifetime mainstay
In 1902 disaster struck. Amélie’s parents were disgraced and financially ruined in a spectacular scandal of national scope, as the unsuspecting employees of a woman whose financial empire was based on fraud. Thanks to his early years in a lawyer’s office, Matisse was able to busy himself to great effect in the organization of his father-in-law’s defense. When all about him lost their heads, burst into tears, and felt more than sorry for themselves, Henri Matisse dealt with their problems one by one. The ordeal had taken its toll, in more than one way. His doctors ordered Matisse to go to Bohain and take two months’ complete rest. Amélie had lost both her hat shop and the apartment on the rue de Châteaudun. For the first time, Henri, Amélie and the three children were united in Bohain, having nowhere else to go.
Hillary Spurling, one of Matisse’s biographers, asserts that Amélie’s memories of that public disgrace nurtured a “suspicion of the outside world” that would always mark the Matisse family. The Matisse family formed a kind of hermetic unit which revolved around the artist’s work and profession. They fitted their activities according his breaks and work sessions. Silence was essential. Even during the years when Matisse lived mostly alone in Nice, an annual ritual of unpacking, stretching, framing and hanging ended with the whole family settling down to respond to the paintings. The conference might last several days. Then the dealers were admitted.
Matisse and his wife had had two sons, Jean (born 1899) and Pierre (born 1900). He was not always in peace with his family. He wrote that their views were not always in accord “which disturbs me considerably in my work, for which I require the most complete calm and from those how surround me, a serenity that I cannot find here. I intend to move to a village a few league away.” Pierre, his brother, Jean, and Marguerite remained close to their father through every vicissitude, and Matisse, in his last invalid years, was devoted to his several grandchildren.
In 1899, at a time when his paintings displayed rebellious talent but not much clear direction, Matisse began attending classes in clay modeling and sculpture. Assigned to copy one of the sculptural masterpieces in the Louvre, he selected Jaguar Devouring a Hare a violently precise work by Antoine-Louis Barye. Later, whenever his paintings seemed stuck, he turned to sculpture to organize his thoughts and sensations.
Influenced by the works of the post-Impressionists Paul Cézanne, Gauguin, Van Goghand Paul Signac, and also by Japanese art, Matisse made color a crucial element of his paintings. Matisse said, “In modern art, it is indubitably to Cézanne that I owe the most.” By studying Cézanne’s fragmented planes — which stretched the idea of the still life to a forced contemplation of color surfaces themselves — Matisse was able to reconstruct his own philosophy of the still life.
Many of his paintings from 1899 to 1905 make use of a pointillist technique adopted from Signac. In 1898, he went to London to study the paintings of J. M. W. Turner and then went on a trip to Corsica.
After years in poverty, Matisse went through his “dark period” (1902-03), moved briefly to naturalism, went back to a dark palette and told friends in 1903 that he had lost all desire to paint and had almost decided to give up.
Fortunately, Matisse was able to earn some money painting a frieze for the World Fair at the Grand Palais in Paris. He also traveled extensively in the early 1900s when tourism was still a new idea. Brought on by railroad, steamships, and other forms of transportation that appeared during the industrial revolution, travel became a popular pursuit. As a cultured tourist, he developed his art with regular doses of travel.

Matisse’s career can be divided into several periods that changed stylistically, but his underlying aim always remained the same: to discover “the essential character of things” and to produce an art “of balance, purity, and serenity,” as he himself put it. The changing studio environments seemed always to have had a significant effect on the style of his work.
In these first years of struggle Matisse set his revolutionary artistic agenda. He disregarded perspective, abolished shadows, repudiating the academic distinction between line and color. He was attempting to overturn a way of seeing evolved and accepted by the Western world for centuries by substituting a conscious subjectivity in the place of the traditional illusion of objectivity .
Matisse hit his stride in the avant-garde art world in the first years of the new decade. He explored the modern art scene through frequent visits to galleries such as Durand-Ruel and Vollard, where he was exposed to work by Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, and Vincent van Gogh.
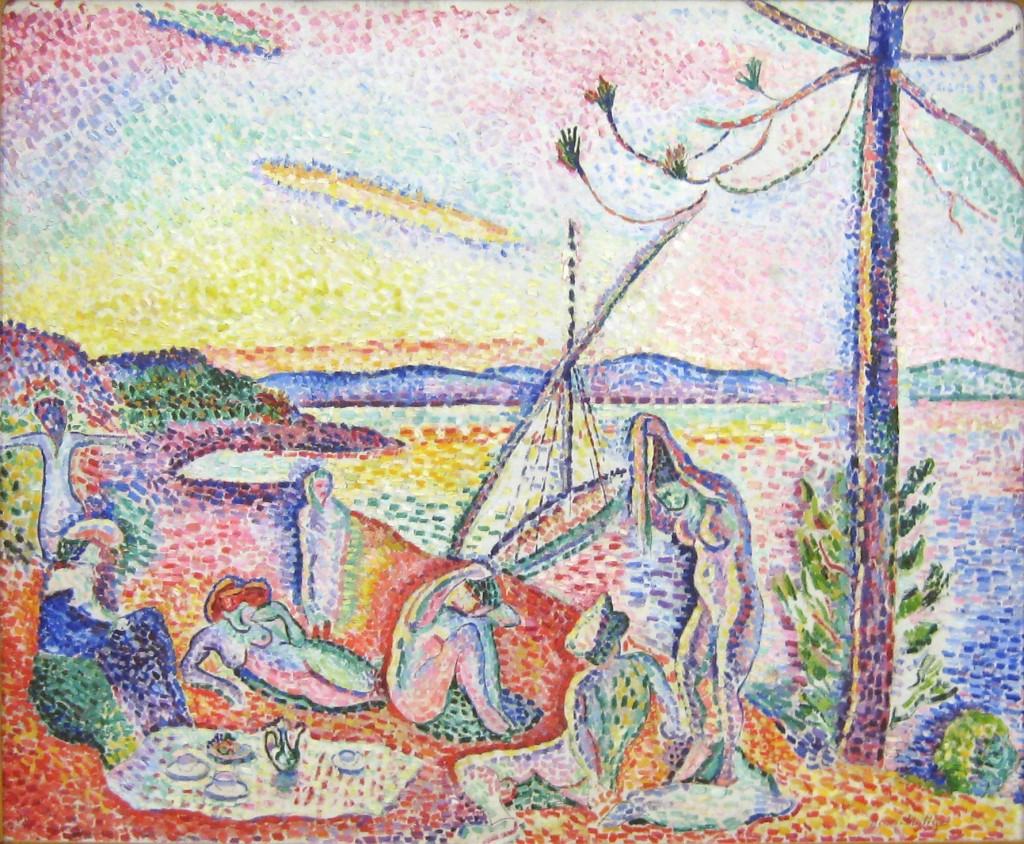
Matisse’s first solo exhibition took place in 1904, without much success. In 16 May 1905 he arrived in the charming Catalan port of Collioure, in the south of France. He soon invited the painter André Derain (1880-1954), 11 years his junior, to join him. By 1905, Matisse was considered spearhead the Fauve movement in France, characterized by its spontaneity and roughness of execution as well as use of raw color straight from the palette to the canvas. Matisse combined pointillist color and Cézanne’s way of structuring pictorial space stroke by stroke to develop Fauvism – a way less of seeing the world than of feeling it with one’s eyes. When the Fauve summer drew to an end, Derain left Collioure with 30 paintings, 20 drawings and some 50 sketches, never to return, while Matisse departed some days later bringing back to Paris 15 finished paintings, 40 aquarelles, over 100 drawings. He returned Collioure in the summers of 1906, 1907, 1911 and 1914. The lure of the sun would prove always to have powers of restoration to the artist throughout his life particularly after periods of great emotional exertion.
When Fauvist works were first exhibited Salon d’Automne in Paris they created a scandal. Eyewitness accounts tell of laughter emanating from room VII where they were displayed. Gertrud Stein, one of Matisse’s most important future supporters, reported that people scratched at the canvases in derision. “A pot of paint has been flung in the face of the public” was the reaction by the critic Camille Mauclair. Louis Vauxcelles described the work with the historic phrase “Donatello au milieu des fauves!” (Donatello among the wild beasts), referring to a Renaissance-type sculpture that shared the room with them. His comment was printed on 17 October 1905 in Gil Blas, a daily newspaper, and passed into popular usage. Derain himself later called the Fauves’ color “sticks of dynamite.” The painting that was singled out for attacks was Matisse’s Woman with a Hat, a portrait of Madame Matisse. This picture was bought be was bought by Gertrude and Leo Stein, a fact which had a very positive effect on Matisse who was suffering demoralization from the bad reception of his work.
Matisse continued his experiments in Collioure, visible in the painting The Open Window and the View of Collioure , also a characteristic work of Fauvism in its raw color and disregard for details. Both of these works of the landscape in the French Mediterranean present a distinct development towards the spontaneous and uninhibited style.
Other than André Derain, Georges Braque, Raoul Dufy and Maurice Vlaminck were also members of the Fauve movement. However, Matisse’s intimate friends among artists were mostly easygoing minor painters, such as Albert Marquet. Matisse’s temperamental aloneness made him prey to vertiginous depressions. He later recalled a breakdown that he underwent in Spain, in 1910: “My bed shook, and from my throat came a little high-pitched cry that I could not stop.”
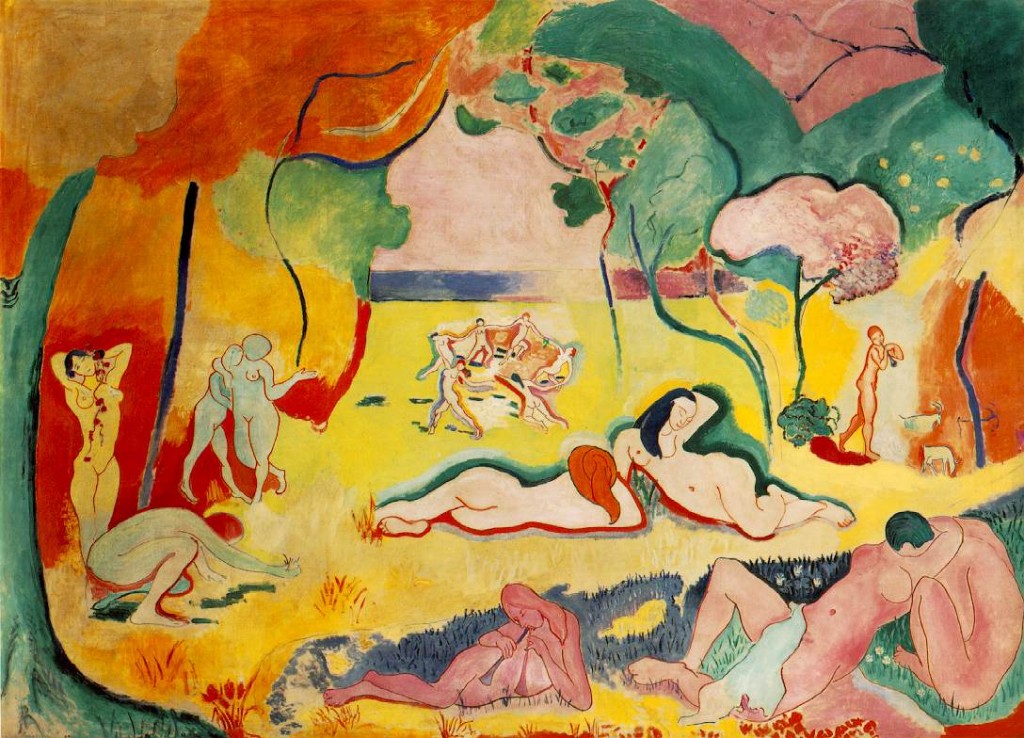
From the onset of is career women were from one of the cardinal motifs of the artist’s production. His Joy of Life (1906) draws us into the world of hallucinatory vividness composed of nymphs set in an idyllic open fields dressed in pure color and sensual outline. Two women lounge in the sunlight while two more chat on the edge of the forest. One crouches to pick some flowers while her companion weaves a chain of them into her hair. A couple embraces each other while another group engages in a lively round-dance in the distance. In this way, Joy of Life depicts woodland nymphs engaging in a celebration of their life, their womanhood, and their sexuality.
Due to the recurrent incidence of nude women and intensely sensual interpretation many observers have assumed that as a man Matisse must have been a hedonist. On the contrary, historic examination demonstrates that in reality, he was rather a self-abnegating Northerner who lived only to work, and did so in chronic anguish, recurrent panic, and amid periodic breakdowns. While Picasso recompensed himself, as he went along, with gratifications of intellectual and erotic play Matisse did not. In an age of ideologies, Matisse dodged all ideas except perhaps one: that art is life by other means.
Matisse’s uninhibited celebration of women is often believed to have initiated from Cézanne’s painting Three Bathers (1882) (which he had acquired for himself along with a Van Gogh and a Gauguin). However, Matisse depicts women as nurturing, welcoming, and unlike the forbidding, massive clay-like presence of those of Paul Cézanne.

The decline of the Fauvist movement, after 1906, did nothing to deter the rise of Matisse. From 1906 -1917 he lived in Paris and established his home, studio, and school at Hôtel Biron. Among his neighbors is sculptor Auguste Rodin, writer Jean Cocteau, and dancer Isadora Duncan. Many of his finest works were created in this period, when he was an active part of the great gathering of artistic talent in Montparnasse, even though he did not quite fit in with his conservative appearance and strict bourgeois work habits. In fact, the aim of Matisse’s art was something less than revolutionary. In 1908, in a famous statement drawn from “Notes of a Painter,” Matisse declared as his ideal an art “for every mental worker, for the businessman as well as the man of letters, for example, a soothing, calming influence on the mind, something like a good armchair which provides relaxation from physical fatigue.”
Matisse’s personal habits were incredibly regular. On a typical day rose early and worked all morning with a second work session after lunch, followed by violin practice, a simple supper (vegetable soup, two hard-boiled eggs, salad and a glass of wine) and an early bedtime.
In 1906, he created a series of 12 lithographs, all variations on the theme of a seated nude. He chose to share his graphic work with the public almost immediately. The lithographs were exhibited at the Druet Gallery in Paris the same year that they were produced, and the woodcuts were shown at the Salon des Independants in the spring of 1907.
In 1907 Appolinaire, commenting about Matisse in an article published in La Falange, said, “We are not here in the presence of an extravagant or an extremist undertaking: Matisse’s art is eminently reasonable.” Notwithstanding newly-won fame, Matisse’s work continued to encounter vehement criticism and it was difficult for him to provide for his family. His controversial 1907 painting Blue Nude was burned in effigy at the Armory Show in Chicago in 1913. Contrary to the fate of the Impressionists, Matisse and other Fauves were able to exhibit in art galleries. In 1908 Paul Cassirer, the German art dealer and editor who played a significant role in the promotion of the work the French Impressionists and Post-Impressionists, staged an exhibit of Matisse’s works in Berlin. In the same year the American photographer Alfred Stieglitz in New York organized him one-man show in his tiny Manhattan gallery called291 which effectively introduced Matisse the powerful American art market.
In the first decade of his notoriety as the leader of the Fauves, Matisse was more admired by foreigners than by the French. It was, after all, the Russians and the Americans who acquired significant collections of his early work almost as quickly as it was created. The great Matisses we see in the Paris museums today were mostly acquired after the artist’s death in lieu of death duties. It took the French a good deal longer to understand Matisse’s greatness-longer, certainly, than the international cadre of aspiring talents that flocked to his classes when he was still one of the most controversial figures in the Paris avant-garde.
In the summer of 1907, Matisse and his wife went on a long trip to italy “for work and Pleasure,” visiting Venice and Padua, where they admired Giotto’s frescos. In Florence the were the guests of the Steins in their villa in Fiesole. From this base matisse visited Arezzo, to study Piero della Francesca, and Siena, attracted by the early Sienese painters, especially, Duccio.

During the first decade of the 20th century Americans in Paris Gertrude Stein, her brothers Leo Stein, Michael Stein and Michael’s wife Sarah took keen interest in Matisse’s art. In addition, Gertrude Stein’s two friends from Baltimore. Clarabel andEtta Cone, became major patrons of Matisse and Picasso, collecting hundreds of their works.The Cone Sisters acquired their first Matisse in 1906 and, during the next four decades, went on to form one of the world’s great collections of his art. The Cone Collection not only contains major works from every phase of Matisse’s long career but reflects the sisters’ special interest in his Nice period, when a new complexity of form and psychology entered the ever intense surface allure of his paintings.
In April of 1906 during a gathering at the house of the legendary Gertrude Stein, Matisse was introduced to Pablo Picasso who was 11 years younger. Picasso and Matisse were poles apart aesthetically and their life styles were no less so. Matisse was markedly taller and more polished than the stocky, cocky Catalan, was then ruler of the turbulent Paris avant-garde art scene. The two were said to have always been looking over their shoulders at each other. It is well-known that after their rivalry grew, sides were taken. Picasso later said: “No one has ever looked at Matisse’s paintings more carefully than I; and no one has looked at mine more carefully than he.”
One key difference between their pictorial concepts was that Matisse drew and painted from nature, while Picasso was much more inclined to work from imagination. The subjects painted most frequently by both artists were women and still lives, with Matisse more likely to place his figures in fully realized interiors.
Gertrude Stein, who loved stirring things up, wrote, “the feeling between the Picassoites and the Matisse-ites became bitter.” Although Matisse dryly noted that “our disputes were always friendly,” it should be pointed out that Picasso and his friends threw suction-cupped darts at Matisse’s 1906 Portrait of Marguerite (which Picasso had obtained in a trade for his own Pitcher, Bowl and Lemon, from 1907). While the rift between the two artists eventually healed, the one between their supporters remained.

In 1909, with the Matisse family lived in a former convent on the Boulevard des Invalides, in Paris, where the artist conducted a painting school. His immense notoriety, which had been confirmed in 1905-06 by Joy of Life, a work which seemed to trash every possible norm of pictorial order and painterly finesse.His friends organized and financed the Académie Matisse in Paris, a private and non-commercial school in which Matisse instructed young artists. It operated from 1911 until 1917.Hans Purrmann and Sarah Stein were several of his most loyal students.
Although it lasted for only three years (1908-11), and yet, during its brief existence the Académie Matisse became one of the principal crossroads of modern painting for a number of gifted European and American artists.
Given the reputation Matisse had acquired as the”wild man” of modernist color, it must have come as a shock to some of his early students that the program of instruction he offered was remarkably conservative. As Jean Heiberg, the first Norwegian to enroll in the Académie, later wrote in a memoir: “The school had, at Matisse’s suggestion, acquired a copy of two antique sculptures from the Louvre, Mars and an archaic sculpture, which he often used to demonstrate. Every now and then he got completely rid of the life model and we only drew from the plaster casts, and his critiques then were no less profitable.”
Among Matisse’s students was Olga Meerson, a Russian Jew who had studied with Wassily Kandinsky in Munich and, already possessed of an elegant style, sought to remake herself under Matisse’s tutelage. Amélie suspected the worst. Perhaps a combination of Amélie’s jealousy and Meerson’s neediness caused a Matisse to end the connection, with bad feeling all around. Meerson moved to Munich, where she married the musician Heinz Pringsheim, a brother-in-law of Thomas Mann. Never having fulfilled her promise as a painter, she committed suicide in Berlin, in 1929. One of Matisse’s biographers, with access to much of the artist’s correspondence, contends that the artist, after his marriage, rarely, if ever, had sex with models, despite his apparent feelings for many.
Two Russian art collectors stood out at the beginning of the 20th century: the cloth merchant Sergei Shchukin (1854–1936) and the textile manufacturer Ivan Morozov(1871–1921). Both acquired modern French art, developed a sensibility for spotting new trends, and publicized them in Russia.
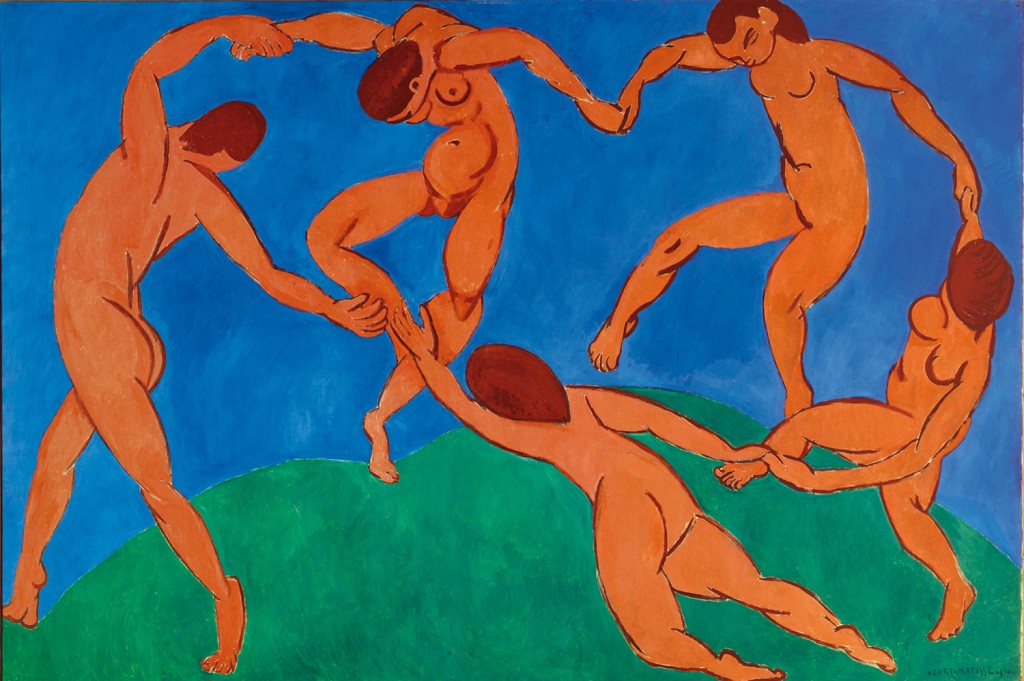
In this period, Matisse had initiated his fecund association with the Russian textile magnate and visionary collector, Sergei Shchukin. The artist created one of his major works La Danse specially for Shchukin as part of a two painting commission. Inspired by a circular dance– perhaps a sardana – performed by fishermen at Collioure, this painting embodies the clash between the sacred and reality. Human hands link together, but they form a divine spirit. Moreover, Matisse all but abandoned perspective The work ’s flatness emphasizes the idea, colors, and material, a notion that made Matisse a model for Modernists. The other painting commissioned wasMusic, 1909.
Shchukin was considered by some almost as a co-producer of some of the artist’s greatest works and was strongly commuted to the French painter’s work. Concerning the violent attacks on his friend, the Russian wrote to the artist: “The public is against you, but the future is yours.” By 1914 Shchukin’s house in Moscow contained thirty-seven Matisses. “He always picked the best,” the artist said.
During the political revolution Lenin expropriated Shchukin collection in person but allowed Shchukin to remain, in servants’ quarters, as caretaker and guide. He died in Paris, in 1936. The collection is now in the Hermitage and Pushkin Museums
From about 1911 to 1915, Matisse struggled with the ideas of Cubism, an experiment he felt he was “not participating in” because it did not “speak to [his] deeply sensory nature.”
Like many avant-garde artists in Paris, Matisse was receptive to a broad range of influences. He is one of the first painters to take an interest in various forms of “primitive” art. His art was profoundly influenced by Easter art as well.
Matisse first flirted with the idea of visiting Morocco after a trip to the Moorish part of Spain in the winter of 1910. This taste of the Moors incited a flame of hope that there would be greater inspiration to paint in Morocco. Furthermore, well aware of the exotic subjects in Morocco that had engendered a wealth of inspiration for the famous French painter Delacroix when he visited the country over eighty years before, Matisse felt Morocco would stimulate his painting genius in ways Europe could not. He strove for neither the picturesque nor the pornographic.
In Morocco, Matisse seems to have had difficulties finding models who would pose for him, particularly women because of the law of the veil. Only Jewesses and prostitutes were exempt. Luckily, Matisse to have found the prostitute Zorah for the purpose although he did not paint her as a prostitute. Instead, in his first picture of her, Zorah en Jaune, sexual themes are most conspicuously absent from the canvas. As a prostitute used to exposing and flaunting her body, Zorah could have easily been painted nude or with less clothing to show herself off, but instead Matisse chooses to keep her clothed and posed with prudence. Unlike the primitive, nude Western women in the Fauve Joy of Life. Moroccan Zorah is clothed with respect and detail to her finer characteristics. He is developing his ability to paint with awareness of the non-sexual qualities of his subject, a movement away from Fauve women.
Many of Matisse’s Moroccan paintings are covered only in the thinnest washes of pigment, as if he wanted the texture of the unpainted canvas to show through so that it would add rawness to the browns and grays.
Matisse’s odalisques have been described as “elaborate fictions” in which the artist re-created the image of the Islamic harem using French models posed in his Nice apartment. The fabrics, screens, carpets, furnishings and costuming recalled the exoticism of the “Orient” and provided a theme for Matisse’s preoccupation with the figure and elaborate patterns of exotic fabrics.
Although Matisse’s interest in textiles are evident in his compositions made during his 1906 trip to Morocco, it didn’t begin as a typical European attraction to the exotic. It was already present to him as a descendent of generations of weavers, who was raised among weavers in Bohain-en-Vermandois, which in the 1880’s and 90’s was a center of production of fancy silks for the Parisian fashion houses. Like virtually all his northern compatriots, he had an inborn appreciation of their texture and design. He understood the properties of weight and hang, he knew how to use pins and paper patterns, and he was supremely confident with scissors.
Matisse was known to be an avid collector of fabrics, from his days as a poor art student in Paris to the latter years of his life, when his Nice studio overflowed with Persian carpets, delicate Arab embroideries, richly hued African wall hangings, and any number of colorful cushions, curtains, costumes, patterned screens, and backcloths. Textiles soon became the springboard for his radical experiments with perspective and an art based on decorative patterning and pure harmonies of color and line. When he moved house, he also moved his fabrics, describing them as “my working library.” He added to the collection all his life, from markets in Algeria, Morocco and Tahiti to the end-of-season sales of Parisian haute couture.
The revitalizing spirit of Morocco would live on in the artist’s imagination until the cutouts of the artist’s last years.


Matisse continued to evolve in unexpected directions even though never became an abstract painter (though some of his most adventurous works, such as the View of Notre Dame of 1914 or the Yellow Curtain of 1916 come close). His motifs were always recognizable, and the tension between the subject and the formal aspects of the painting was a central concept of his artistic ideal.
Matisse moved to Nice in 1917 to distance himself from wartime activity, where bright, warm colors showed him “simpler venues which won’t stifle the spirit.” His spirit became loyal to the “silver clarity of light” in Nice, and he returned to Paris only for a few months each summer. The years 1917–30 are known as his early Nice period, when his principal subject remained the female figure or an odalisque dressed in oriental costume or in various stages of undress, depicted as standing, seated, or reclining in a luxurious, exotic interior of Matisse’s own creation. These paintings are infused with southern light, bright colors, and a profusion of decorative patterns. They emanate the atmosphere suggestive of a harem.
In 1929, Matisse temporarily suspended easel painting and traveled to America to sit on the jury of the 29th Carnegie International and, in 1930, spent some time in Tahiti and New York as well as Baltimore, Maryland and Merion, Pennsylvania.He was especially thrilled with New York. An important collector of modern art, and owner of the largest Matisse holdings in America, Dr. Albert Barnes of Merion, commissioned the artist to paint a large mural for the two-story picture gallery of his mansion. Matisse chose the subject of the dance, a theme that had preoccupied him since his early Fauve masterpiece Joy of Life.
Americans were prominent among Matisse’s patrons throughout his career, beginning with the Steins (Leo Stein bought Joy of Life right out of the Salon in 1906) and including the Cone sisters of Baltimore and the notoriously cantankerous Barnes. The foundational Matisse monograph was written during his lifetime by another American, Alfred Barr. Also important in promoting Matisse’s presence before the transatlantic public was the Manhattan gallery founded in 1931 by the artist’s son, Pierre, who remained a prominent figure in the New York art world for almost six decades. In addition to his father, he represented Balthus, Calder, Dubuffet, Giacometti, Miro, Tanguy and others, many of them also friends.
Throughout his long and productive career, Matisse periodically refreshed his creative energies by turning from painting to drawing, sculpture and other forms of artistic expression. In his lifetime he also produced 12 illustrated books which were known as “livre d’artiste” (artist’s book), a specific type of illustrated book that became common in France around the turn of the century. These books were deluxe, limited editions, meant to be collected and admired as works of art, as well as, read. This process began when Swiss publisher Albert Skira first approached the modern master in 1930 to illustrate the work, Poesies, by 19th century French symbolist poet Stéphane Mallarmé . Matisse responded to Skira’s invitation with great enthusiasm and that summer, devoted most of his attention to the commission while he was residing in Paris. The result was a collection of 29 beautiful etchings, of which the Museum will display 16. The subject matter, like the poems themselves, varies considerably, although many of the images reflect the artist’s vacation to the South Pacific. Matisse’s etchings of Mallarmé’s poems are considered among his greatest works in the print medium. In 1941, again for Skira, Matisse began one of his most complicated and successful printmaking projects, Florilege des Amours de Ronsard, illustrating the love poems of 16th century French Renaissance poet Pierre de Ronsard. Ronsard’s subject and strong imagery lent themselves gracefully to Matisse’s favored themes of fruits, flowers, the female form and portraits. The artist selected the poems himself and translated the work from Renaissance French to contemporary French for the publication of the anthology

For all his long-lasting friendships with other artists, famous and obscure, Matisse’s days and nights were absorbed by solitary labor. Playing the violin seemed a more intimate consolation for decades of critical abuse than the affections of his wife and children.
Although their marriage was still somewhat fragile, the Matisses had decided to stay on in Nice when their lease expired at Place Charles-Félix in the summer of 1938.
Matisse and his wife were separated in 1939 after 41 years when Amélie tried to dismiss the coolly efficient young Lydia Delectorskaya, an orphan refugee from Siberia, who had been hired as Amélie’s companion. However, the Matisses’ marriage ran afoul not of any romantic rival but for the artist’s wish to stand on his own. The first climax came years before in 1913, when Amélie sat more than a hundred times for the Portrait of Madame Matisse. A friend’s diary reported at the time. “Crazy! weeping! By night he recites the Lord’s Prayer! By day he quarrels with his wife!” The portrait, which was the last work to enter Shchukin’s collection, caused Matisse “palpitations, high blood pressure and a constant drumming in his ears.” Such frenzy was not rare when Matisse had difficulty with a painting. He referred to the painting years later in a letter to her as “the one that made you cry, but in which you look so pretty.” Amélie ceded routine leadership of the family to Marguerite. The 1913 portrait was his last painting of her.
Matisse and his wife met the last time to discuss details of their legal separation, in July 1939. One of its key provisions was that everything would be divided equally between the couple.
The meeting took place in Paris at the Gare St. Lazare and lasted thirty minutes, during which Amélie Matisse kept up a flow of small talk while her husband.”My wife never looked at me, but I didn’t take my eyes off her…,” Matisse wrote on the night of that final encounter: “I couldn’t get a word out…. I remained as if carved out of wood, swearing never to be caught that way again.” “I’m going to try to isolate myself as if I were still absent,” Matisse announced on his first return to Paris since the official separation from his wife, ‘rarely leaving his apartment except for visits to the cinema (his first color film, starring Danny Kaye, was a revelation).”
After her dismissal, Delectorskaya shot herself in the chest with a pistol, remarkably with only a slight effect. Soon after the artist and his wife were legally separated Delectorskaya was back. She arrived with a bouquet of white daisies and blue cornflowers from her Aunt’s garden on July 15th, St Henry’s Day. Their working collaboration was to last right up to Matisse’s death in 1954. Her will throughout was indomitable; she typed, kept records and meticulous accounts and paid the household bills. She also organized Matisse’s correspondence and coordinated his business affairs with an iron grip as well as being his studio assistant and muse. And when called upon, even scoured the countryside on her bike for provisions during the war. Matisse claimed that his entire household came to a standstill in her absence which, in the light of what Lydia accomplished is anything, if not an understatement.
In the face of the family’s icy resentment, the Russian said of Matisse, “He knew how to take possession of people and make them feel they were indispensable. That was how it was for me, and that was how it had been for Mme. Matisse.”
Life with Matisse must have been taxing but it had been Amélie’s chosen vocation, through years of their studio-centered homes. Her central role in the artist’s life was security, which Shchukin’s patronage provided, along with a sizable house in Issy-les-Moulineaux, where the family moved in 1909. However, in this period Matisse was increasingly absent. In 1930, his travels took him to the United States, where he was thrilled by New York, and to Tahiti.
Matisse found that Tahiti was “both superb and boring . . . There the weather is beautiful at sunrise and it does not change until night. Such immutable happiness is tiring.” He dived off the reefs and never forgot the colors of the madrepores and the absinthe-green water; these appear in cut-outs like Polynesia, 1946, or The Bird and the Shark, 1947, as images of a spectacular and, on the whole, beneficent nature.
In September of 1940 he employed a temporary stand-in for his regular night nurse. The agency sent him a young, twenty-one year old student nurse: Monique Bourgeois. After a year in nursing school she made her way to Nice to find work at the nursing school placement office. She was in luck. An artist by the name of Henri Matisse was looking for a temporary night nurse. On September 26, 1942 she rang the bell to Matisse’s apartment in Cimiez. Lydia answered.
Monique propped up Matisse’s pillows, read to him and took walks with him, and her impish wit and straightforward conversation enchanted him. She quickly became comfortable with Matisse and soon their conversations turned more personal. Matisse spoke of himself, his family and his grandchildren whom he adored. When Matisse was able to, he got out of bed and showed Monique his studio and paintings. She cared for him for 15 nights, during which time he had several attacks in a row of severe stomach pains.The return of Matisse’s regular night nurse drew an end to Monique’s duties.
Matisse painted four canvases of her, as well as numerous sketches with charcoal or ink. She would sit in a pretty but rather uncomfortable straightbacked wooden seat for two or three hours at a time. Short periods of rest, no more than a quarter of an hour, were spent in total silence sipping a cup of tea. Their work together culminated in March 1943 with the painting of Tabac Royal. When her assignment ended, he asked her to pose for him, and she reluctantly consented. “I was rather surprised, for I had never been considered a beauty,” she wrote in a 1993 book about their friendship. “I never really noticed whether he was in love with me,” she said in a 1992 interview inParis-Match magazine. “I was a little like his granddaughter or his muse, but he was always a perfect gentleman.”
Monique’s career then changed dramatically, as she took the veil on September 8, 1944 and given the name of Sister Jacques-Marie. Matisse objected strenuously to Bourgeois’ decision to enter the convent but reconciled with her and eventually determined to bring to fruition the sisters’ dream of a chapel for their convent. She did not see Matisse again for two years.
Matisse may have realized late in life that he had burdened his sons with the sort of hectoring pressures to meet his standards that he had suffered from his own father. Pierre, of the boy in The Piano Lesson said of , “Yes, it was me, and you have no idea how much I detested those piano lessons.” It has been the conventional wisdom that Matisse was not able to carry into his family relationships the success he achieved in his art, and that this dysfunction extended to his son Pierre. However, 829 letters, which can run as long as 21 pages, give a different impression of the relationship of father and son. After Henri’s permanent separation from his wife, Pierre became his father’s indispensable confidant. The old man writes his son, ”You are the only member of the family with whom I can communicate”; and again, touchingly, ”What would become of me, if you were no longer here?”
Although Matisse never granted exclusive rights to his son to show his paintings, he was intimately involved in the Pierre Matisse Gallery as a business, guiding his son’s career from Pierre’s first courageous days as an ambitious immigrant of 24. ”You have to arrive with every possible advantage and hold your own against everything and everyone,” Pierre writes his father. ”American jealousy is terrible, and it has none of the outward politeness of French jealousy.”
Marguerite had married a brilliant man of letters, Georges Duthuit, who was Matisse’s best critic in his lifetime; when Duthuit proved unfaithful to her, the artist forbade him to write about his work. Matisse is never so affecting as in his account of the two weeks that Marguerite spent with him after her escape in 1945.
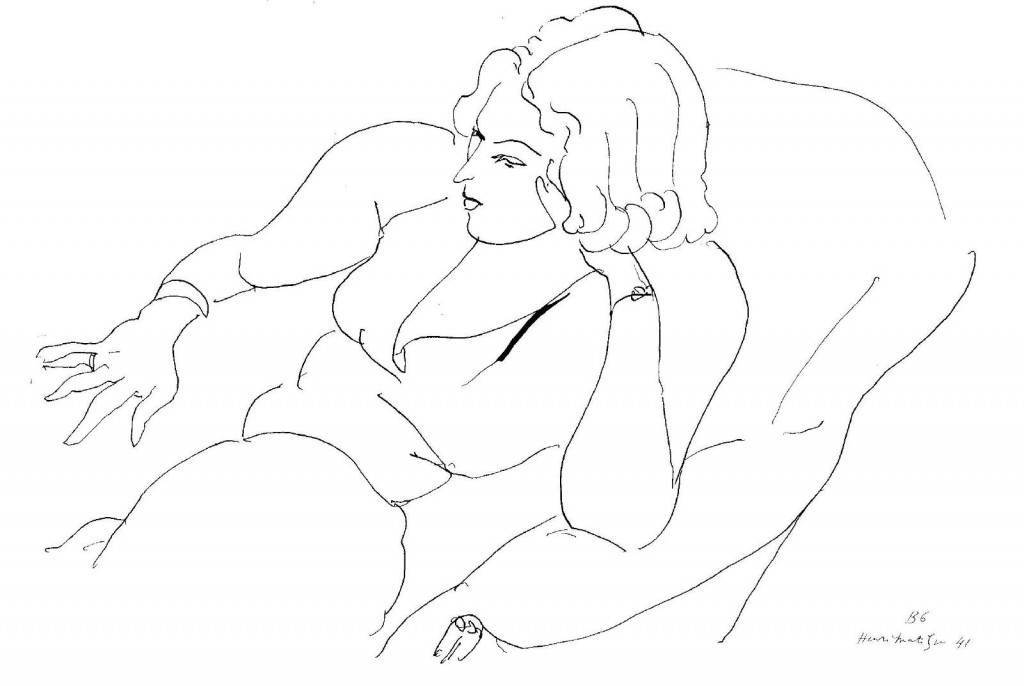

Matisse experimented drawing throughout his lifetime often helping him to work out compositional and stylistic problems or new ideas. During the mid-1930s, he created distinctive series of pen-and-ink drawings on the subject of the artist and his model, while in the early 1940s he conceived his famous sequences of Thèmes et Variations, sensitively drawn spare works in elegant, unshaded line, describing simplified forms of female figures or still lifes. In the late 1940s and early ’50s, his drawings become bolder, the contour line thicker, the forms even more simplified and devoid of detail.
Sculpture was another medium pursued by Matisse since his early years, and although independent in expression, it was frequently used to find a solution to pictorial problems or became an inspiration to painting.“I sculpted as a painter,” said Matisse, “I did not sculpt like a sculptor.” In relief sculpture, he could deal with the mass and form of the body in real space, and at the same time clarify his sense of how to represent the human form on canvas. We might say that the woman represented in this relief stands between the realms of sculpture and painting, or between three-dimensional reality and the flatness of painted representation. More than half of Matisse’s sculptures were completed between 1900 and 1910; he also frequently worked in series, manipulating the form and simplifying it over the years. Among his best-known works belong the series of four Back reliefs (1903–31), the series of five Jeannetteheads (1910–16), and the Large Seated Nude (1925–29).
Matisse is quoted extensively about his art. He most likely spoke about his own experience as an artist in a 1941 letter to Pierre, referring to a particularly harrowing painting by his friend Georges Rouault: “A man who makes pictures like the one we were looking at is an unhappy creature, tormented day and night. He relieves himself of his passion in his pictures, but also in spite of himself on the people round him. That is what normal people never understand. They want to enjoy the artists’ products—as one might enjoy cows’ milk—but they can’t put up with the inconvenience, the mud and the flies.”


Much of Matisse’s source of inspiration was poetic. Like his art, the poetry or poetic prose Matisse loved was intimate, sensuous and personal. In his later years he developed the practice of reading poetry early each day before he raised a paint brush, pencil or etching needle. His sources were French medieval poetry of Charles d’Orléans and Pierre de Ronsard, as well as the more avant-garde writings of Stéphane Mallarmé, Henri de Montherlant, Louis Aragon and others. Matisse noted that poetry was like oxygen: “just as when you leap out of bed you fill your lungs with fresh air.” This kept him young at heart — like a sensual elixir of youth.
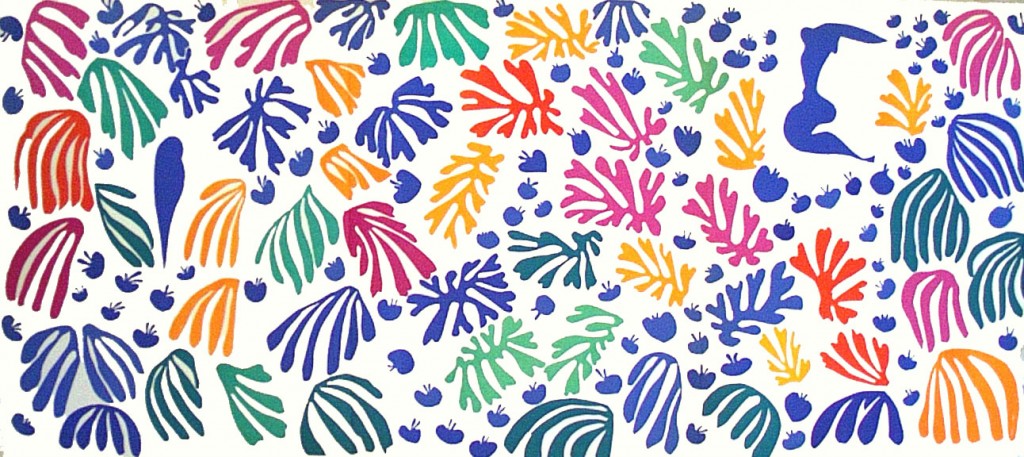
He made hundreds of drawings, original prints and illustrated books. This last art form included what Matisse called his ‘flower books’. These were beautiful objects in themselves, inspired by the tradition of the Medieval manuscript. Faces, body parts, lovers, fruit and flowers reveal Matisse’s exquisite arabesque lines, along with an extraordinary sense of color. For the celebrated Jazz for instance, the images are characterized by brilliant colors, swirling lines and arabesques form series of jewel-like shapes, in themes which range from the circus to female forms amongst the sea. Matisse made his images from colored stencils based on paper cut-outs.
In 1941 Matisse was diagnosed with cancer and, following surgery, he started using a wheelchair. Before undergoing a risky operation in Lyon, he wrote an anxious letter to his son, Pierre, insisting, “I love my family, truly, dearly and profoundly.” He left another letter, to be delivered in the event of his death, making peace with Amélie.
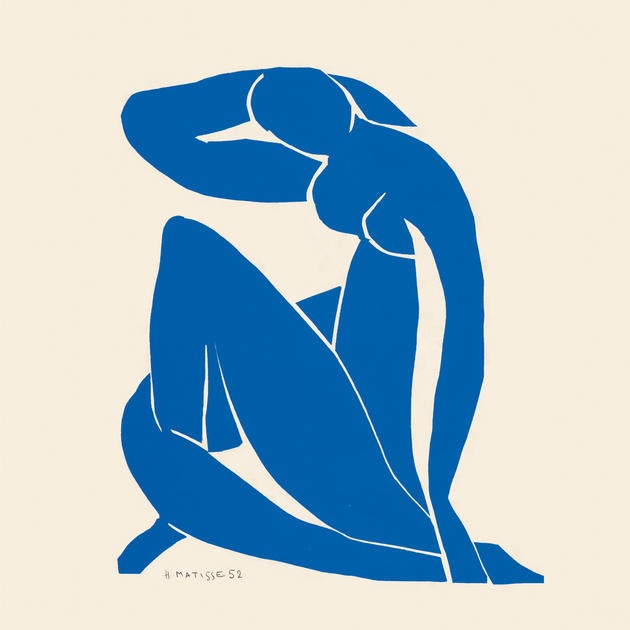
However, Matisse’s extraordinary creativity could not be dampened. “Une seconde vie”, a second life, was what he called the last fourteen years of his life. Following and operation he found renewed and unexpected energies. This new lease of life led to an extraordinary burst of expression, the culmination of half a century of work, but also to a radical renewal that made it possible for him to create what he had always struggled for: “I have needed all that time to reach the stage where I can say what I want to say.” Until his death he would be cared for Lydia Delectorskaya, who had also modeled for the artist numerous times. With the aid of assistants he set about creating cut paper collages , often on a large scale, called gouaches découpés. By maneuvering scissors through prepared sheets of paper, he inaugurated a new phase of his career. The cut-out was not an abdication from painting and sculpting: he called it “painting with scissors.” Matisse said, “Only what I created after the illness constitutes my real self: free, liberated.” Moreover, experimentation with cut-outs offered Matisse innumerable opportunities to fashion a new, aesthetically pleasing environment: “You see as I am obliged to remain often in bed because of the state of my health, I have made a little garden all around me where I can walk… There are leaves, fruits, a bird.” In 1947 he published Jazz , a limited-edition book containing prints of colorful paper cut collages, accompanied by his written thoughts. In the 1940s he also worked as a graphic artist and produced black-and-white illustrations for several books. “The walls of my bedroom are covered with cutouts,” he wrote to Rouveyre in 1948. “I still don’t know what I’ll do with them.”

In 1941, his son Pierre, reported that Matisse had undergone a serious operation. Friends tried to persuade the aging artist to leave France, but Matisse said, “If all the talented people left France, the country would be much poorer. I began an artist’s life very poor, and I am not afraid to be poor again. . . . Art has its value; it is a search after truth and truth is all that counts.”
World War II ushered in an utter collapse of Matisse’s life structures: his health, his marriage and the unknown fate of his pictures in Russia as well as in occupied France.
In 1943, to escape the threat of an allied bombardment of Nice, Henri Matisse moved into the Villa Le Rêve , on the outskirts of Vence. Built in 1930 for an English family, this was to be his home and studio for the next five years, and here he not only painted and drew but also created the Jazz series of paper cut-outs. Matisse described this process as “drawing with scissors” explaining: “Paper cutouts allow me to draw in colon I see it as a simplification. Instead of drawing the contour and putting color into it–one modifying the other–I draw directly in color.” Completed between 1943 and 1944, the 20 collaged paper cutouts for Jazz were translated into pochoirs(stencils), which were then printed and published in an edition of 270 in 1947. The subject matter of the plates in Jazz ranges from the circus to mythology to nature. The plates are accompanied by text composed and handwritten by the artist himself. Matisse intended that the text. which expounds upon the role of the artist serve a primarily visual function.
Matisse’s love for his doves and his cats Minouche and Coussi were touchingly evident in a series of photographs taken at Villa Le Rêveby Helene Adant, a cousin of Lydia Delectorskaya. Matisse’s passion for birds (and especially doves) began during the summer of 1936. Back in Paris and strolling along the banks of the river Seine, his
attention was drawn to the merchants selling a variety of caged song birds and doves. He’d returned home with five or six birds at a time and delighted in their shapes and colors, plumage and singing. His love of birds lasted the rest of his life. Nearing the end of his day, Matisse gave Picasso, who loved birds and had canaries and pigeons of his own, the last of his fancy pigeons. Picasso drew its portrait on the famous poster, Dove of Peace.
During the war, Matisse was isolated and rarely expressed his political sentiments and shielded his art from politics under all circumstances. It is known that created the reverberant domestic idyll The Piano Lesson in the summer of 1916, while death swaggered at Verdun. During the Second World War the French Resistance had affected the two most important women in his life, Amélie and Marguerite. Marguerite was a typist for the Communist underground, and Marguerite, who served as a courier—as well as his son Jean, who was involved in sabotage operations. (Pierre had by that time become an art dealer in New York.) Amélie was jailed for six months; Marguerite was tortured by the Gestapo but escaped from a cattle car that was stalled on its way to a prison camp in Germany during the war’s chaotic waning months. Matisse, thoroughly unpolitical, was shocked when he heard that his daughter Marguerite had been.
In the years 1941-1954 Matisse engaged in a unique correspondence with the French satirical draughtsman and writer André Rouveyre (1879-1962) , in which his ongoing production and innovation are reflected and refracted. It is perhaps the most beautiful correspondence of the 20th century and tells the story of a significant friendship. Matisse and Rouveyre met as young students at the ‘Ecole des Beaux-Art in Paris at the end of the 1890s, but the courses of their lives quickly became very different, and their paths diverged to a great extent over the subsequent years. Only when they coincidentally met again during the war, after Matisse’s operation, did their close friendship develop. Despite the conspicuous differences between them, Rouveyre, as is evident from the correspondence, came to follow Matisse’s working process at close quarters.
The correspondence stands out from all others in its extent and frequency – for long periods they wrote to each other daily, sometimes several times a day – and in its abundance of drawings, sketches and decorated envelopes by Matisse. The letters, which are typified by intimacy and irresistible humor, speak of both the events of everyday life and Matisse’s work and thus provide us with unique insight into the artist’s creative process and his thoughts on his life and work.
Toward the end of his life, Matisse experienced a renewed burst of creativity in a series of works of unexampled purity, refinement and freedom–manifestations of a true “late style.” Matisse’s creativity extended into the area of graphic arts and book illustration, the latter begun when he was already in his sixties, with the illustrations to Stéphane Mallarmé’s Poésies (1932).
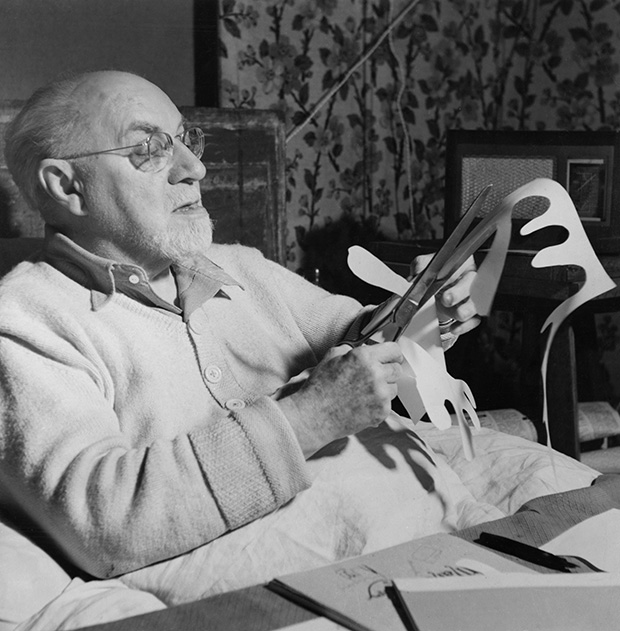

In 1951, Matisse completed a monumental four-year project of designing the interior, the glass windows and the decorations of the Chapelle du Rosaire in Vence. This project horrified the Catholic hierarchy but also the contemporary art world then largely influenced by Communist dogma. Picasso is often said to have recommended that Matisse decorate a brothel instead. This project was the result of the close friendship between Matisse and Sister Jacques-Marie.
Press coverage wasn’t always so helpful, and reporters sensationalized the relationship between the artist and the nun. Sister Jacques-Marie maintains that nothing untoward ever happened between them. But their deep fondness for one another is evident in her conversation and in read snippets of his correspondence.
Sister Jacques-Marie met Matisse in 1942, when she was a student nurse named Monique Bourgeois and Matisse, in his early 70’s and recovering from intestinal cancer, advertised for a “young and pretty night nurse.”
Matisse’s prestige was such that he could largely financed the project himself and after it was completed, the chapel opened in 1951 in a ceremony led by the Archbishop of Nice. At first bewildered, the sisters of the convent came to love its chaste serenity and effulgent color. While he worked models and assistants were jealously guarded, cut off from outside contact and more or less confined to the premises. Picasso, accompanied by his lover, Françoise Gilot, was a frequent and welcome visitor. While still fencing with each other like old duelists, they talked art.
The Chapel had taken four years to complete and had exhausted Matisse, who by then was unable to stand for long periods and had to attach his paint brush to a long pole. But in his home, sitting on his bed or in a wheelchair, he continued to make gouache cutouts. After Rouveyre teased him for embracing religion, Matisse urged his friend to look at his cutout of a naked woman, Zulma, at the May Salon in Paris in 1950: “You will see the awakening of the converted,” was his retort.
La Gerbe, multicolored leaves that resemble a spray of flowers, was completed a few months before his death, but it explodes with life. The artist who almost reinvented color in painting had by now found freedom in the simplicity of decoration. “I have the mastery of it,” he told Rouveyre in a letter. “I am sure of it.”
In 1952 the Musée Matisse is inaugurated at the artist’s birthplace of Le Cateau–Cambrésis to which he donated 100 of his works – valued at up to $14,000,000.
Matisse died of a heart attack at the age of eighty-four, on November 3, 1954, with Marguerite and Delectorskaya at his side. Lydia Delectorskaya left immediately with the suitcase she had kept packed for fifteen years. He is interred in the cemetery of the Monastère Notre Dame de Cimiez and a Musée Matisse was opened in the area.

